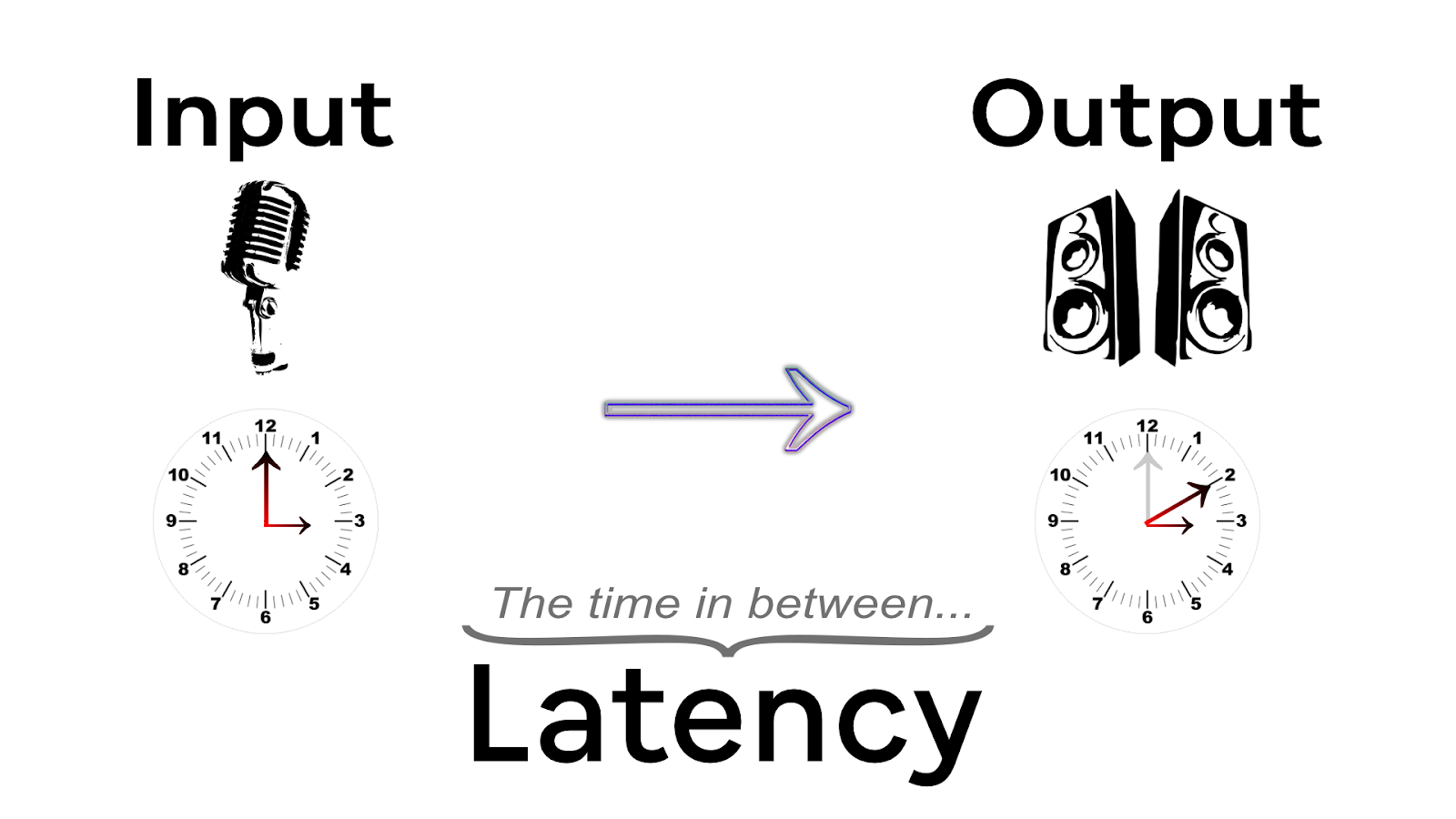
什么音频延迟
音频延迟,简单理解就是音频从输入系统到输出系统的时间差。
可以有很多种表现形式,比如在网络通话场景,说话方的声音到达接听方,经过的时间;或者在玩游戏的时候,手指按下了枪的扳机,到你听到枪声。
在不同的系统上,在软件、硬件设备上,都会出现,是一个通用的现象。从某种意义上来说,存在且不可避免。
因为所谓的实时性通常都不是指零误差,零延时,而是针对你的使用场景,满足一定期望以内的时延即可以称之为实时。
参考:https://help.ableton.com/hc/en-us/articles/360010545559-How-Latency-Works
Latency refers to a short period of delay between when a signal enters a system, and when it emerges from it.
Latency cannot be avoided, but it can be understood!
音频延迟怎么产生的
音频延迟的产生,在数字音频来看,就是两个原因:信号处理,音频buffer。
In digital audio, latency is introduced by signal conversion and audio buffers within the signal path.
How-Latency-Works
信号处理
包含ADC、DAC转换,这是数字音频的入口和出口。
音频buffer
在硬件或者软件通路上,用于临时存储音频数据的区域,在通路中从上一个节点传递到下一个节点。
哪里会发生音频延迟
- The audio interface
- The audio interface driver
- The operating system (which may require additional time to process and mix streams from other applications before passing it out to the speakers)
- Between the Audio Interface and the DAW
- In the DAW’s signal processing (eg. monitored tracks / native effects / plug-ins / etc.)
音频延迟计算
Buffer Size (number of samples) ÷ Sample Rate (kHz) = Expected Latency (ms).
For example, while running with a Buffer Size of 256 samples and a Sample Rate of 44.1 kHz,
an audio interface will convert the incoming signal with 5.8 milliseconds of expected latency before sending it into Live (256 samples ÷ 44.1 kHz).